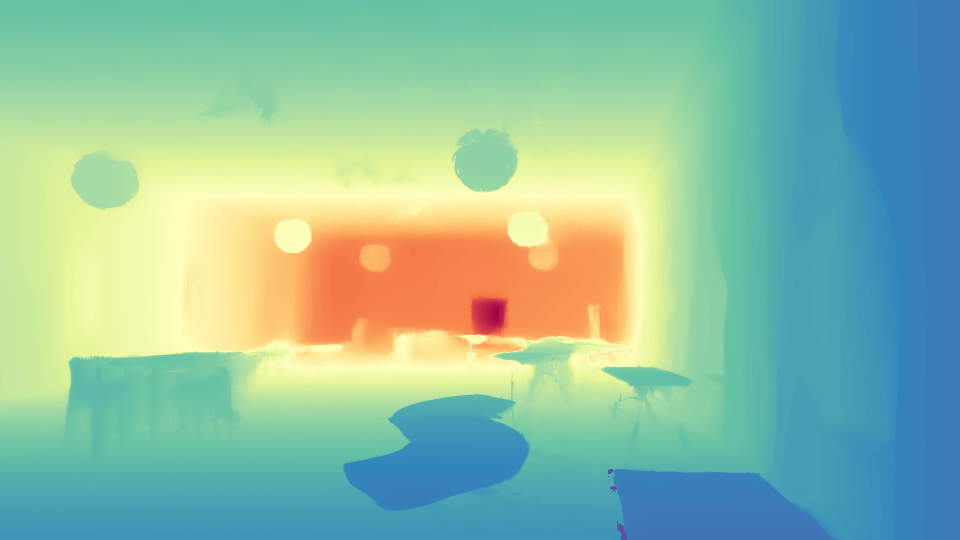
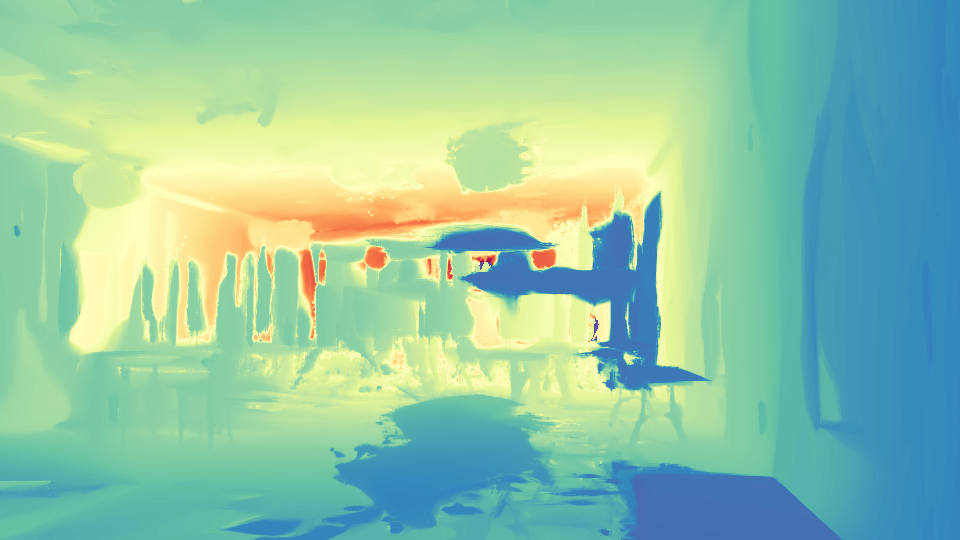
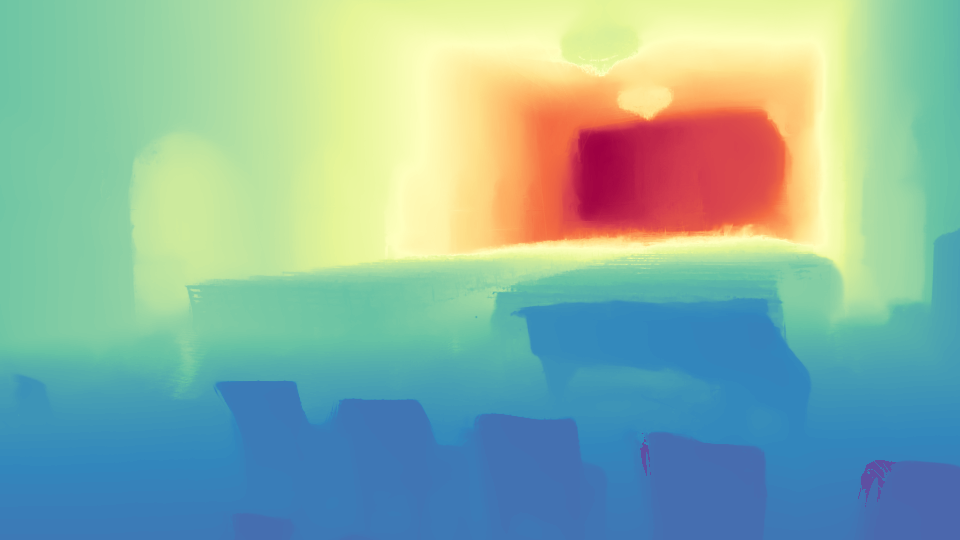
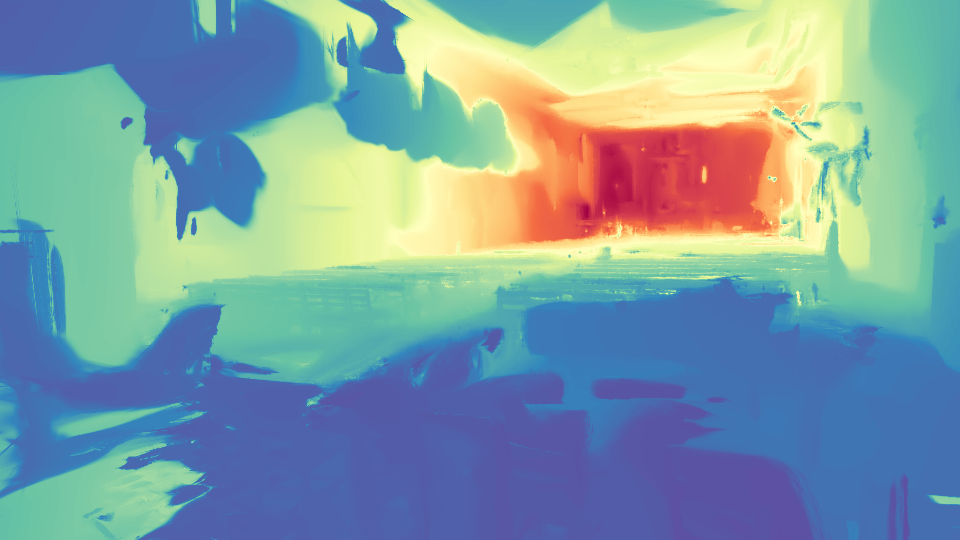






The results shown are derived from 3 training views. Our method estimates poses, which are then interpolated to render the video.
We present InstantSplat, a method for photorealistic 3D reconstruction from extremely sparse views, with robust optimization completing in a few seconds. We achieve this by combining rich geometric priors from a feed-forward model with point-based representations (e.g., 3D Gaussian Splatting), eliminating the need for Structure-from-Motion (SfM), which is often unreliable and slow. To this end, InstantSplat adopts a self-supervised optimization framework that jointly updates the 3D scene representation and camera poses by unprojecting 2D pixels into 3D and aligning them through differentiable neural rendering. However, during optimization, pixel-aligned predictions from the feed-forward model are often redundant in overlapping regions, or may be unreliable in ambiguous parts. We address these issues with a co-visibility-based initialization that effciently prunes redundant overlap and enhance spatial coverage, together with a confidence-aware optimization that dynamically adjusts per-point gradients based on point-wise uncertainty to improve convergence. Together, these components align all learnable scene parameters through neural rendering. Overall, InstantSplat achieves over 30 times faster reconstruction than COLMAP with 3D-GS while improving visual fidelity. We also maintain compatibility with various point-based representations for both view synthesis and surface reconstruction.
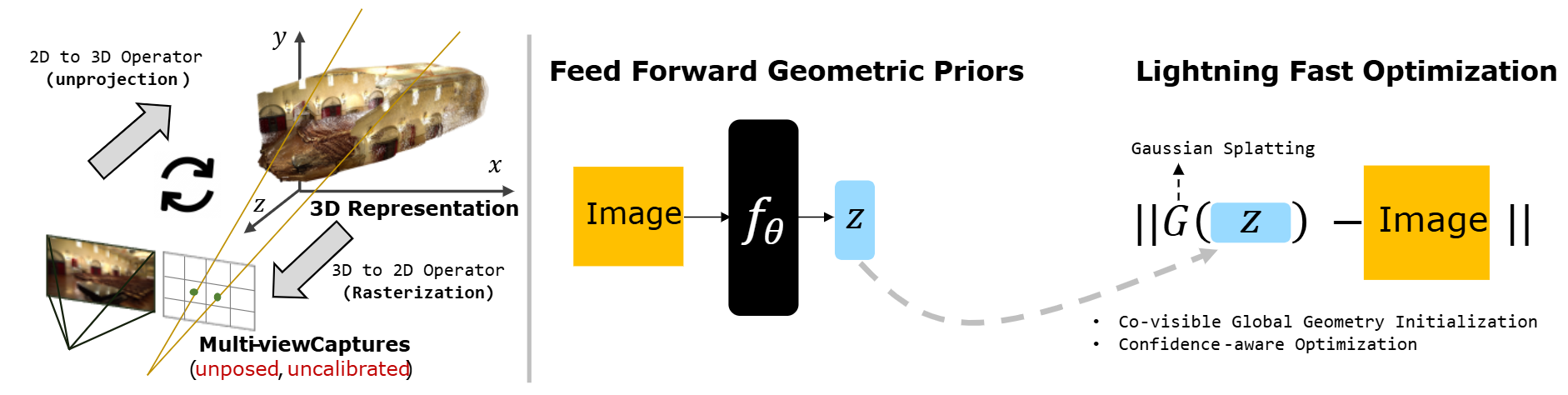
Overall Framework. InstantSplat synergizes the geometry priors from the foudation models, employs Co-visible Global Geometry Initialization, and utilizes Gaussian Splatting to jointly optimize camera parameters and the 3D scenes with confidence-aware optimizer.
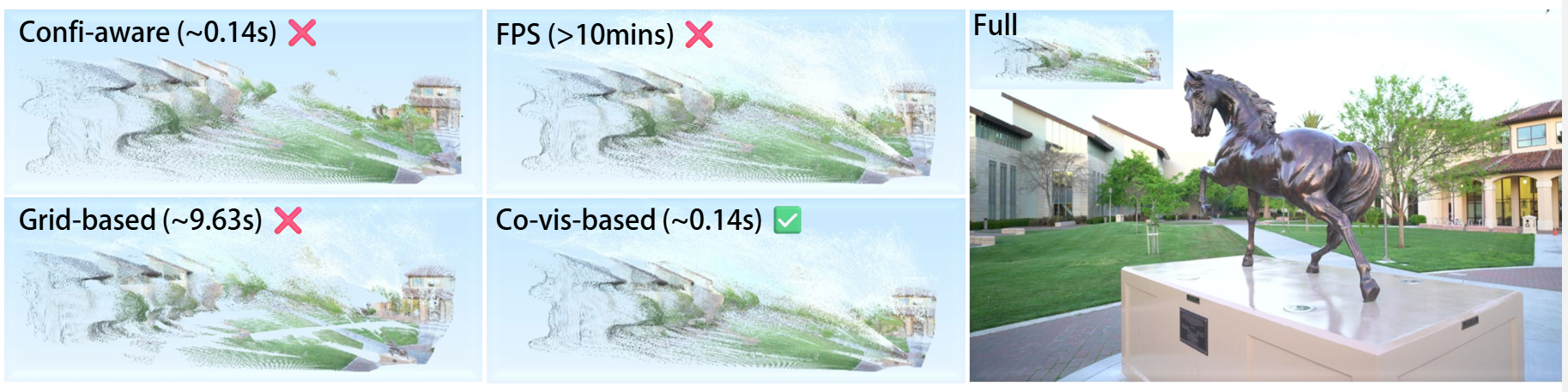

Before/after visualizations of different downsampling trategies. Directly downsampling by the predicted confidence map yields missing blocks despite an 8×8×8 scene partition. Farthest point sampling (FPS) improves coverage but is too slow in practice. These observations motivate an adaptive, efficiencyaware sampling method.
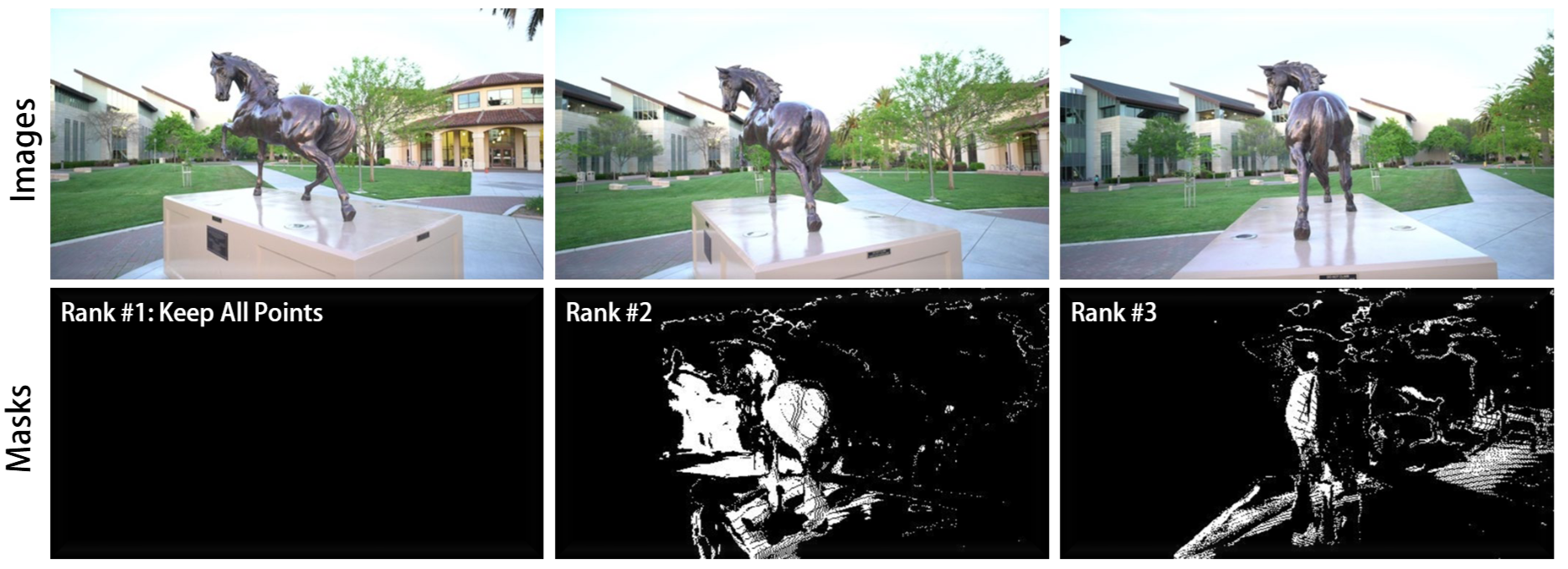

Co-visible Geometry Initialization.. Given multiple views, we rank them based on average confidence scores and apply co-visibility pruning to remove redundant points. The highestranked view (left) retains all predicted points, while lower-ranked views (middle, right) are masked by projecting higher-confidence points and eliminating overlapping regions. This process maximizes geometric coverage and reduces redundant 3D primitives for efficient joint optimization.

InstantSplat rapidly reconstructs a dense 3D model from sparse-view images. Instead of relying on traditional Structure-from-Motion poses and the complex adaptive density control strategy of 3D-GS, which is fragile under sparse-view conditions, we propose to synergize the geometric foundation model (i.e., MASt3R for dense yet less accurate initialization along with a fast alignment step to jointly optimize camera poses and the 3D scenes. It supports various 3D representations, including 2D-GS, 3D-GS, and Mip-Splatting.

















@misc{fan2024instantsplat,
title={InstantSplat: Sparse-view Gaussian Splatting in Seconds},
author={Zhiwen Fan and Kairun Wen and Wenyan Cong and Kevin Wang and Jian Zhang and Xinghao Ding and Danfei Xu and Boris Ivanovic and Marco Pavone and Georgios Pavlakos and Zhangyang Wang and Yue Wang},
year={2024},
eprint={2403.20309},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}